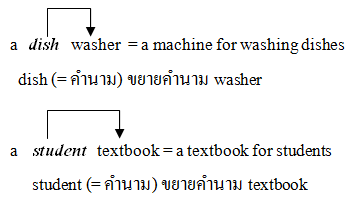
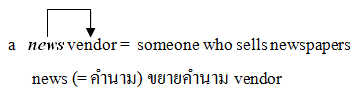คำคุณศัพท์ (adjective)
คำคุณศัพท์ คือ คำที่ใช้ขยายคำนาม และสรรพนาม เพื่อแสดงให้เราเห็นถึงคุณสมบัติของคำนามและสรรพนามได้ชัดเจนยิ่งขึ้น จะวางไว้หลัง Be หรืออยู่หน้าคำนามที่ใช้ขยาย
ลักษณะของคำคุณศัพท์
1) คำคุณศัพท์บางคำเกิดจากการเติม suffix เช่น -ish -ary -y -ous -ious -al-ic/-ical
-like -ful –less ท้ายคำนามบางคำ และ –ive -ent/-ant -able/-ible ท้ายคำกริยาบางคำ เช่น
|
Noun
|
Adjective
|
Verb
|
Adjective
|
|
child
|
childish
|
attract
|
attractive |
|
moment
|
momentary
|
excel
|
excellent
|
|
cloud
|
cloudy
|
please
|
pleasant
|
|
danger
|
dangerous
|
accept
|
acceptable
|
|
space
|
spacious
|
comprehend
|
comprehensible
|
|
tradition
|
traditional
|
atmosphere
|
atmospheric
|
|
practice
|
practical
|
||
|
child
|
childlike
|
||
|
power
|
powerful
|
||
|
power
|
powerless
|
2) คำคุณศัพท์มีรูปเดียว ไม่มีรูปเอกพจน์ (singular form) หรือรูปพหูพจน์ (plural form) และไม่เปลี่ยนรูปคำนามที่คำคุณศัพท์นั้นขยาย คำคุณศัพท์แต่ละคำสามารถใช้กับคำนามที่เป็นรูปเอกพจน์และรูปพหูพจน์ได้ อีกทั้งคำคุณศัพท์ส่วนมากใช้กับคำนามได้ทุกเพศ เช่น
that small boy those small boys
this old book these old books
a young boy a young girl
a young man a young woman
3) คำคุณศัพท์มีทั้งที่เป็นคำเดียวโดด ๆ เช่น small, long, old มักจะต้องวางไว้หน้าคำนาม เช่น
The old gentleman gave the small boy some money.
4) คำคุณศัพท์ประสม (compound adjective) เช่น red-haired เป็นต้น มีโครงสร้างต่าง ๆ เช่น
|
5) คำบางประเภทที่นำมาใช้เป็นคำขยาย ทำหน้าที่เป็นคำคุณศัพท์ เช่น
|
คำที่อยู่ข้างหน้าจะทำหน้าที่เหมือนคำคุณศัพท์ เช่น คำนามที่อยู่ข้างหน้าส่วนมากไม่ต้องเติม s ให้เป็นพหูพจน์ แต่คำนามใดที่มี s อยู่แล้ว ไม่ต้องตัด s ทิ้ง เช่น
 |
ตำแหน่งของคำคุณศัพท์
คำคุณศัพท์ส่วนมากที่เป็นคำโดด คำคุณศัพท์ประสม หรือคำประเภทอื่นที่ทำหน้าที่เป็นคำขยาย มีตำแหน่งต่าง ๆ ดังนี้
1) วางไว้หน้าคำนามและหลังคำกำกับนาม เช่น
a naughty boy a beautiful flower some old books
a newly-constructed building the time-consuming task
the stolen money the lost ring a frying pan
2) ตามหลัง verb ‘BE’ เช่น
Those children are healthy and strong.
3) ตามหลัง linking verbs (seem, appear, become, sound, look, turn, grow, remain,
prove, etc.) เช่น
The weather seems nice today.
I hope the weather will remain nice and cool like this for months.
การจัดลำดับคำคุณศัพท์
เมื่อต้องการใช้คำคุณศัพท์หลาย ๆ คำขยายคำนามคำเดียว ต้องเรียงลำดับคำคุณศัพท์ตามการบอกลักษณะดังนี้
|
คำกำกับนาม (determiner) |
ลำดับที่ (rank) |
จำนวน (number) |
คุณภาพ (quality) |
ขนาด/รูปร่าง (size/shape) |
สี (color) |
ที่มา (origin) |
วัสดุที่ใช้ (material) |
จุดประสงค์การใช้ (purpose) |
คำนาม (noun) |
|
his those the boy’s |
first – first |
two three five |
nice modem classic |
– big – |
brown blue – |
Italian – English |
leather wooden
|
walking – reading |
shoes houses books |
การเรียงลำดับคำคุณศัพท์ ส่วนมากจะวางคำคุณศัพท์ตามลำดับในตารางนี้ แต่บางครั้งก็มีการวางสลับที่กันและไม่จำเป็นที่จะต้องมีคำคุณศัพท์ทุกชนิดใส่ไว้ในประโยคเดียวกัน การใช้คำคุณศัพท์ขึ้นอยู่กับผู้พูด/ผู้เขียนว่าต้องการจะอธิบายอะไรเกี่ยวกับคำนาม
Ref.School of Liberal Arts. Sukhothai Thammathirat Open University.